Solutions
Microsoft Warehouse Management
In today's fast-paced world, businesses rely heavily on efficient and organized warehouse management to ensure a seamless flow of goods from receipt to distribution. It encompasses the planning, control, and coordination of all activities occurring within a warehouse, ensuring timely and accurate order fulfillment.
What is Warehouse Management and How Does it Work?
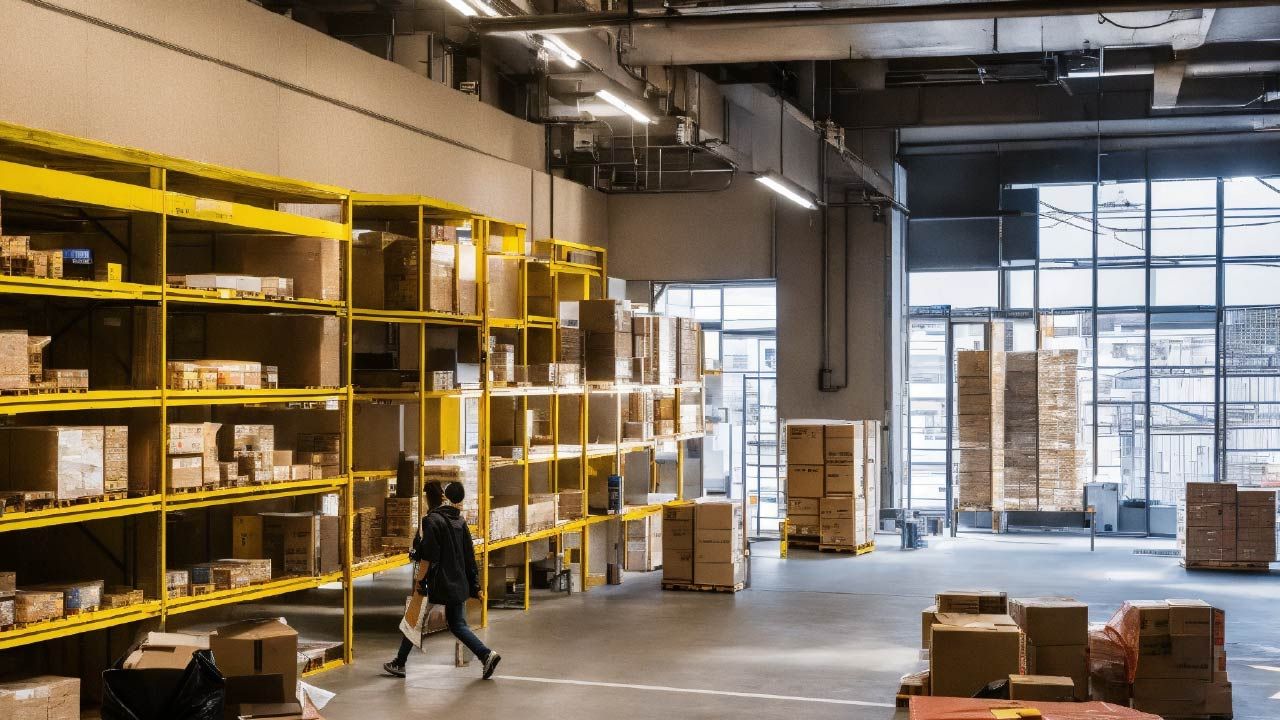

Warehouse management involves several key functions:
- Warehouse design and layout: Optimizing space utilization for efficient product movement, storage, and picking processes.
- Inventory receiving and put-away: Verifying incoming shipments, logging data, and storing items in designated locations within the warehouse.
- Inventory storage and retrieval: Employing various storage methods (e.g., racking systems, palletization) and retrieval techniques (e.g., forklifts, picking robots) to manage stock efficiently.
- Order fulfillment: Picking, packing, and shipping orders accurately and efficiently, ensuring timely delivery to customers.
- Inventory control: Maintaining accurate inventory records, tracking stock levels, and implementing reorder points to avoid stockouts.
Benefits of Effective Warehouse Management:
- Improved Efficiency: Optimized layout, streamlined processes, and proper inventory management lead to faster order fulfillment and reduced labor costs.
- Reduced Costs: Minimized storage space waste, improved inventory control, and fewer stockouts contribute to cost savings.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Accurate and timely order fulfillment leads to happier customers, boosting brand reputation and loyalty.
- Increased Profitability: By optimizing processes and reducing costs, effective warehouse management translates to improved profitability for the business.
Key Elements of a Warehouse Management System (WMS):
Many warehouses utilize Warehouse Management Systems (WMS):
- Software solutions: WMS automates tasks, tracks inventory in real-time, and optimizes picking and packing processes.
- Data tracking and reporting: Provides detailed reports on inventory levels, order fulfillment times, and performance metrics for continuous improvement.
- Integration with other systems: Connects seamlessly with accounting software, sales platforms, and transportation management systems for a unified data flow.
Advanced Technologies Transforming Warehousing

- Robotics and Automation: From autonomous picking robots to conveyor systems and automated guided vehicles (AGVs), these technologies vastly improve efficiency in moving and sorting goods.
- Internet of Things (IoT): By equipping warehouses with sensors and connected devices, managers gain real-time visibility into inventory levels, equipment status, and environmental conditions (temperature, humidity), allowing for preventative maintenance and quick response to issues.
- RFID (Radio Frequency Identification): RFID tags and readers enable automatic identification and tracking of inventory, eliminating manual barcode scanning and reducing errors.
- Predictive Analytics and Machine Learning: Forecasting demand patterns, optimizing inventory allocation, and anticipating disruptions to help managers make proactive decisions and avoid costly stockouts.
The Evolution of Warehouse Management Systems (WMS)
Beyond core inventory and order management, modern WMS solutions often encompass:
- Labor Management: Tracking worker productivity, optimizing labor allocation, and facilitating efficient task allocation.
- Yard Management: Scheduling incoming and outgoing shipments, coordinating truck movements within the warehouse yard, streamlining loading/unloading processes.
- 3D Warehouse Visualization: Virtual modeling of your warehouse to experiment with changes in layout and workflow for maximum space utilization.
- Transportation Route Optimization: Integration with transportation management systems to determine the most cost-effective shipping routes and carriers.
Tailoring Warehouse Management Strategies
The optimal balance of technology and processes depends on several factors:
- Size and Scale: Small facilities might still rely on spreadsheets. Larger operations with high order volumes benefit the most from advanced WMS and automation.
- Type of Product: Handling perishables, hazardous materials, or fragile goods requires specialized storage and handling considerations.
- Industry-Specific Needs: E-commerce fulfillment may prioritize rapid order picking, while manufacturing storage focuses on raw materials and component management.
Questions to Ask Yourself
- Current Challenges: Are you struggling with manual processes, inventory inaccuracies, or delays in order fulfillment?
- Growth Projections: Do you anticipate a significant increase in order volume or warehouse capacity?
- Technology Budget: Are you prepared to invest in advanced solutions like robotics, IoT sensors, or a fully-featured WMS?
Conclusion:
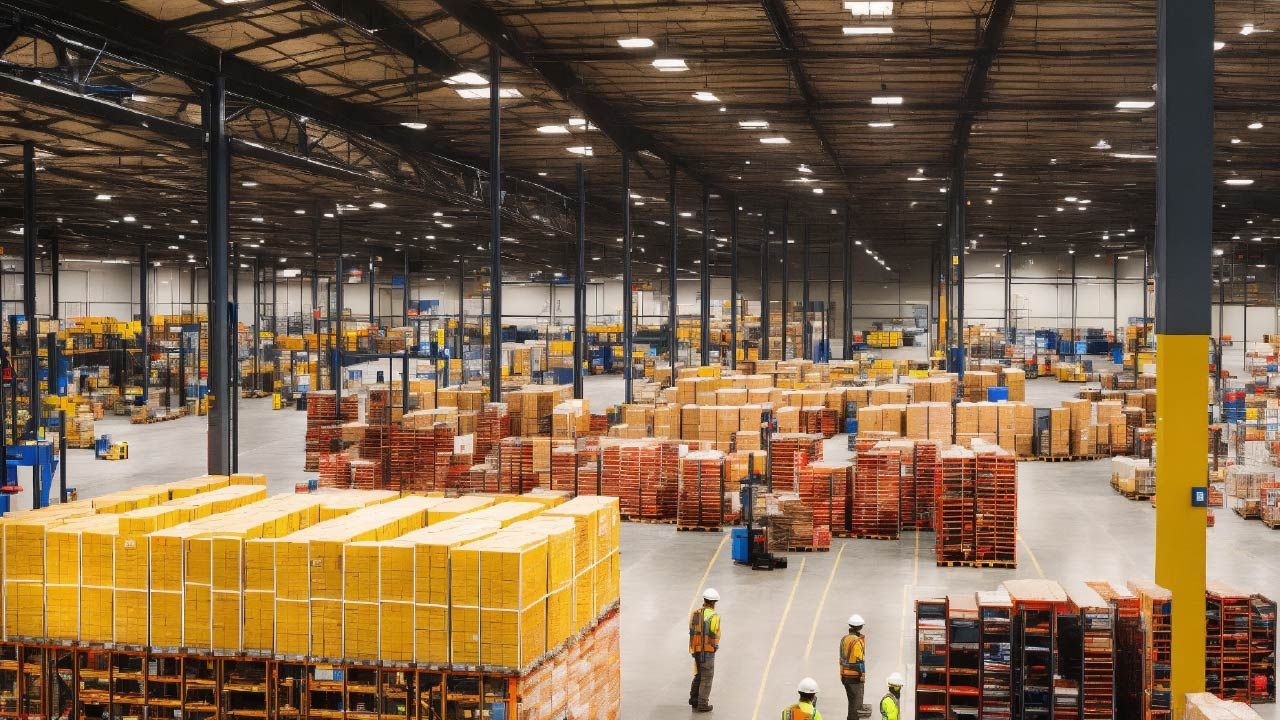

Effective warehouse management acts as the backbone of a successful supply chain. By implementing best practices, utilizing technology, and continuously optimizing processes, businesses can ensure efficient and cost-effective storage, retrieval, and distribution of goods, ultimately contributing to overall business success.
